- What is an example of autonomy vs shame and doubt?
- What are typical infant behaviors that illustrate the autonomy versus shame doubt stage of Erikson’s theory?
- What is autonomy vs shame?
- What is Erikson’s trust vs mistrust theory?
- What are the 5 developmental stages?
- What are the 2 aspects of development?
- What are common development goals?
- What do you mean by mixed goals?
- What are conflicting goals?
What is an example of autonomy vs shame and doubt?
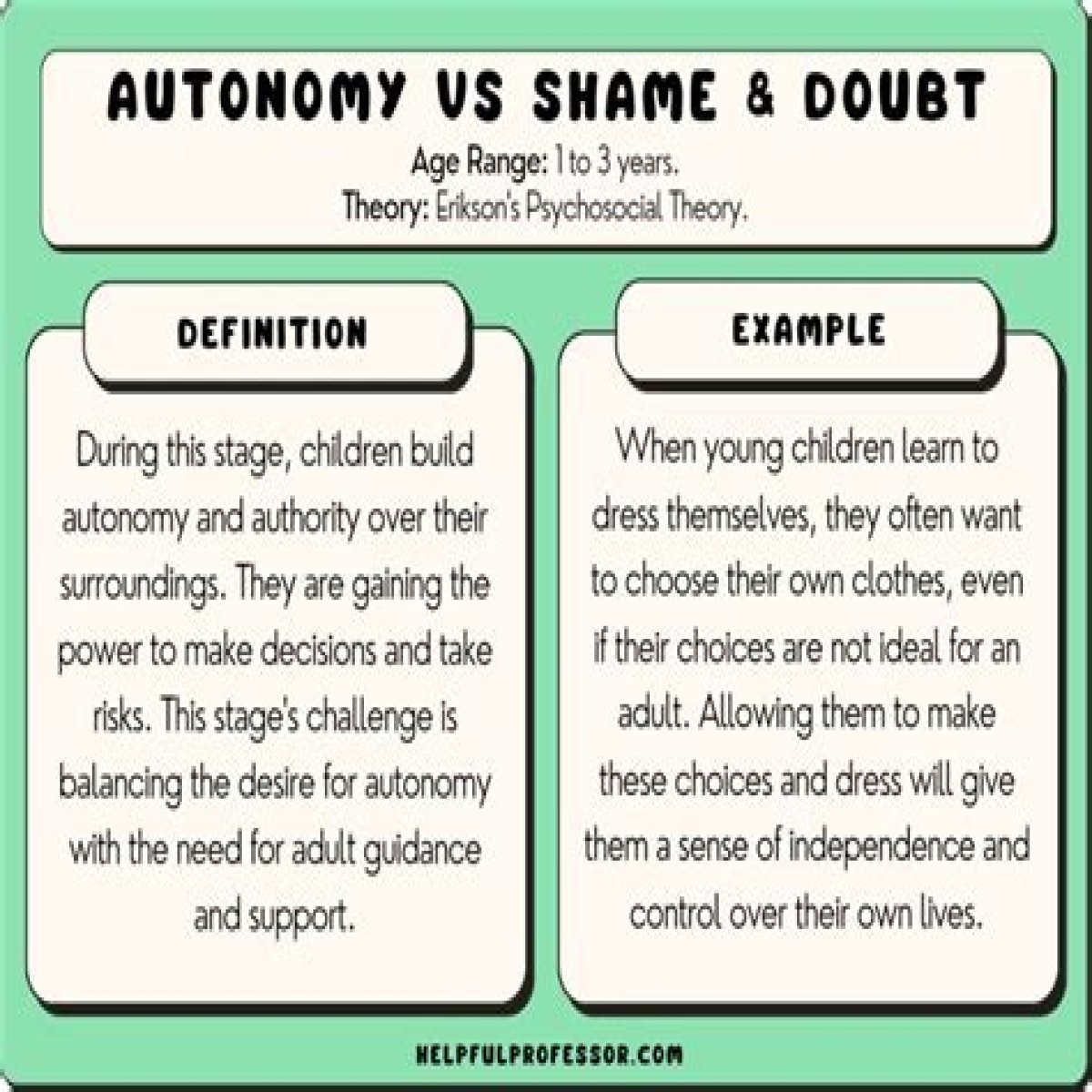
Autonomy vs. shame and doubt by working to establish independence. This is the “me do it” stage. For example, we might observe a budding sense of autonomy in a 2-year-old child who wants to choose her clothes and dress herself.
Which of the following stages coincides with Erik Erikson’s stage of autonomy vs shame and doubt?
Erikson’s stages within this period are triggered by the new, physical, cognitive, or social skills of the child rather than by changes in sexual sensitivity as Freud suggested. Erikson’s stage of autonomy versus shame and doubt centers around the toddler’s new mobility and the accompanying desire for autonomy.
What are typical infant behaviors that illustrate the autonomy versus shame doubt stage of Erikson’s theory?
What are typical infant behaviors that illustrate the “autonomy versus shame/doubt” stage of Erikson’s theory? At this point in development, not only can infants walk, but they can also climb, open and close, drop, push and pull, and hold and let go.
What age is trust vs mistrust?
Trust vs. mistrust [Birth-2] is the first stage in Erik Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development. This stage begins at birth and continues to approximately 18/24 months of age.
What is autonomy vs shame?
Autonomy versus shame and doubt is the second stage of Erik Erikson’s stages of psychosocial development. This stage occurs between the ages of 18 months to around age 2 or 3 years. According to Erikson, children at this stage are focused on developing a greater sense of self-control.
What is basic trust vs mistrust?
Trust vs. mistrust is the first stage in Erik Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development. If the care the infant receives is consistent, predictable and reliable, they will develop a sense of trust which will carry with them to other relationships, and they will be able to feel secure even when threatened.
What is Erikson’s trust vs mistrust theory?
Failure to develop trust will result in fear and a belief that the world is inconsistent and unpredictable. During the first stage of psychosocial development, children develop a sense of trust when caregivers provide reliability, care, and affection. A lack of this will lead to mistrust.
Why is trust vs mistrust important?
The trust versus mistrust stage serves as a foundation of development. The outcomes of this stage can have effects that influence the rest of an individual’s life. Because of this, it is essential for parents to provide responsive, dependable care.
What are the 5 developmental stages?
Five Stages of Child Development
- Newborn. During the first month of life, newborns exhibit automatic responses to external stimuli.
- Infant. Infants develop new abilities quickly in the first year of life.
- Toddler.
- Preschool.
- School age.
How important are the first 5 years of life?
Children’s early experiences and relationships in the first five years of life are critical for development. In the early years, your child’s main way of learning and developing is through play. Other influences on development include genes, nutrition, physical activity, health and community.
What are the 2 aspects of development?
Development is a positive growth or change in economical, social and political aspects of a country. Two aspects of development are: (a) Economic development or rise in income of people. (b) Social development, which includes education, health and public services.
Why do people look at a mix of goals for development?
1 Answer. For development, people do look at a mix of goals-which not only focus on seeking/earning more income but also on non-material aspects like equal treatment, respect of other, dignity of labour, a safe and secure work environment, pollution free surroundings etc.
What are common development goals?
Answer
- Equality in the society in which we live.
- Increase in Income.
- Good Medical Facility.
- Stock of basic necessities.
- Good Education.
What are the mixed goals of development?
It means that development is mix up of all the goals like freedom,peace,harmony,repect towards others,income and many more.
What do you mean by mixed goals?
Why do different persons have different notions of development?
Answer: (b) Different persons have different notions of development because life situations of persons are different. Development goals of a girl from a rich urban family will be surely different from a farmer in Rajasthan. It is because their situations, lifestyle and status are very different from each other.
What are conflicting goals?
Conflicting goals are goals that block other’s implementation. Explanation: For example, A person has multiple goals set out in mind. But certain goals are intermixing and becoming a hindrance to one another. They are called conflicting goals.
What should be the developmental goal of a country?
The Developmental goals for countries like India are: 1) Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger. 2) Achieve universal primary education. 3) Promote gender equality and empower women.